组合(Composite)模式,又叫做树形模式,主要用来处理树形结构数据。是将一组对象组织成树形结构,以表示一种“部分-整体”的层次结构。让客户端可以统一单个对象和组合对象的处理逻辑。
组合模式通过以树形结构来表示“部分-整体”,使得用户对叶对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性。也就是说在组合模式中,整个树形结构的对象都属于同一种类型,用户可以对叶对象和组合对象统一处理。
组合模式主要有透明式和安全式两种分类,下面来分别说明
在该方式中,抽象构件声明了所有子类中的全部方法,这样实现抽象构件接口的所有子类都具备了全部方法,这样的好处是叶节点和枝节点对于外界没有任何区别,它们具备了完全一致的接口。但是对于叶节点有些本身不具备的方法,就可能会有安全隐患(空指针异常等)。其结构类图如下所示:
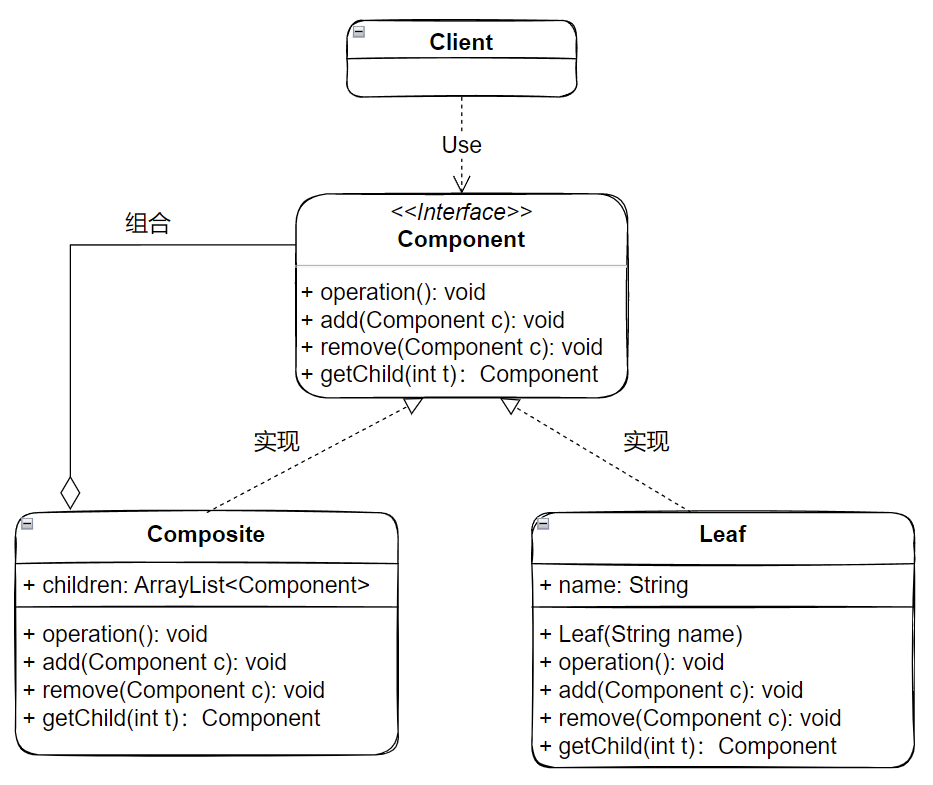
Component:抽象构件,为叶节点和树枝节点声明公共接口,以及访问和管理子类的接口Composite:树枝构件,组合中的分支节点对象,作用是存储和管理子部件Leaf:树叶构件,组合中的叶节点对象,用于继承和实现抽象构件Client:客户端前面提到透明式组合模式中,因为抽象构件声明所有子类方法,有可能会造成安全问题。所以在安全式中,将管理叶节点的方法转移到树枝构件中,抽象构件和树叶构件没有对子对象的管理方法,这样就避免了透明式组合模式中的安全问题。但是由于树叶和树枝构件有不同的接口,因此在使用时,就不能将两种构件一概而论,对于客户端调用方而言,就失去了透明性。其结构类图如下所示:
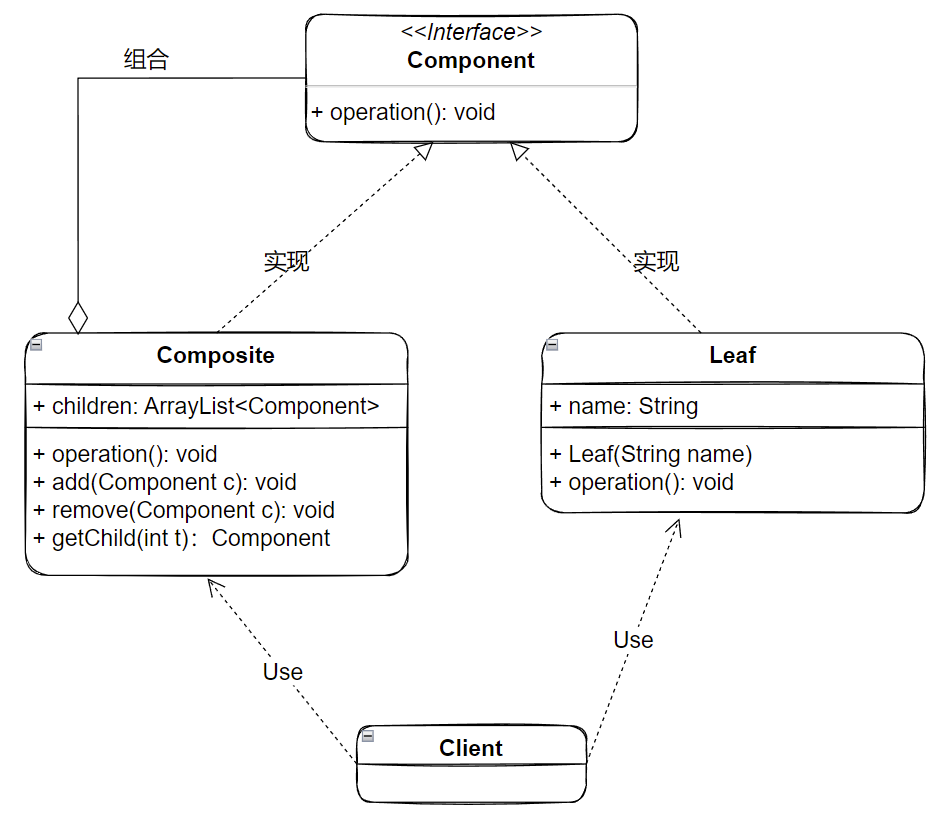
Component:抽象构件,为叶节点和树枝节点声明公共接口,没有访问和管理子类的接口Composite:树枝构件,组合中的分支节点对象,作用是存储和管理子部件Leaf:树叶构件,组合中的叶节点对象,没有对子类的管理方法Client:客户端根据上面的类图,可以实现如下代码:
/** * @description: 透明式抽象构件 * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/3 */ public interface Component { /**公共操作方法**/ void operation(); /** * 添加构件 * @param c 组合模式中的构件 */ void add(Component c); /** * 移除构件 * @param c 组合模式中的构件 */ void remove(Component c); /** * 获得子对象 * @param t 子对象序号 * @return 子对象 */ Component getChild(int t); } /** * @description: 树枝节点 * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/3 */ public class Composite implements Component{ private ArrayList<Component> children = new ArrayList<>(); @Override public void operation() { for (Component child : children) { child.operation(); } } @Override public void add(Component c) { children.add(c); } @Override public void remove(Component c) { children.remove(c); } @Override public Component getChild(int t) { return children.get(t); } } /** * @description: 树叶节点 * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/3 */ public class Leaf implements Component{ private String name; public Leaf(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public void operation() { System.out.println("我是树叶节点:" + name); } @Override public void add(Component c) { } @Override public void remove(Component c) { } @Override public Component getChild(int t) { return null; } } /** * @description: 客户端类 * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/3 */ public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { Component component = new Composite(); Component leaf1 = new Leaf("1"); Component leaf2 = new Leaf("2"); component.add(leaf1); component.add(leaf2); component.operation(); component.getChild(1).operation(); //这里树叶构件能调用add方法就会造成安全隐患 leaf1.add(leaf1); } }客户端运行结果:
我是树叶节点:1 我是树叶节点:2 我是树叶节点:2/** * @description: 安全式抽象构件 * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/3 */ public interface Component { /**公共操作方法**/ void operation(); } /** * @description: 树枝节点 * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/3 */ public class Composite implements Component{ private ArrayList<Component> children = new ArrayList<>(); @Override public void operation() { for (Component child : children) { child.operation(); } } public void add(Component c) { children.add(c); } public void remove(Component c) { children.remove(c); } public Component getChild(int t) { return children.get(t); } } /** * @description: 树叶节点 * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/3 */ public class Leaf implements Component{ private String name; public Leaf(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public void operation() { System.out.println("我是树叶节点:" + name); } } /** * @description: 客户端类 * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/3 */ public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { Composite composite = new Composite(); Leaf leaf1 = new Leaf("1"); Leaf leaf2 = new Leaf("2"); composite.add(leaf1); composite.add(leaf2); composite.operation(); } }客户端测试结果:
我是树叶节点:1 我是树叶节点:2组合模式常见的应用场景主要是出现树形结构的地方,比如文件目录,公司人员架构图等等
比如按照部门和员工组织成树形结构,可以统一处理薪资:
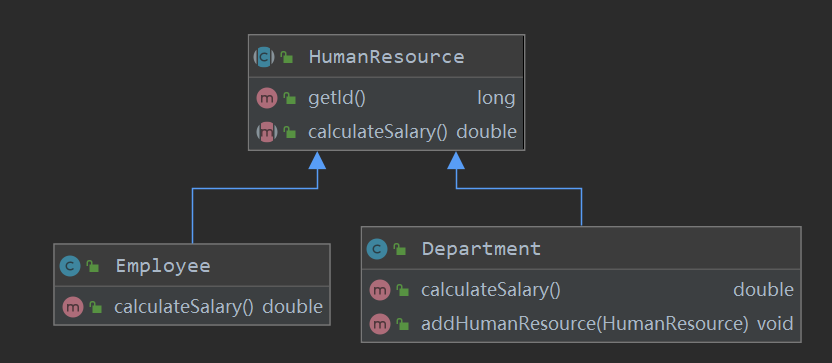
/** * @description: 人力资源抽象构件 * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/3 */ public abstract class HumanResource { protected long id; protected double salary; public HumanResource(long id) { this.id = id; } public long getId() { return id; } /** * 计算工资 * @return 工资结果 */ public abstract double calculateSalary(); } /** * @description: 部门树枝构件 * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/3 */ public class Department extends HumanResource{ private List<HumanResource> humanResources = new ArrayList<>(); public Department(long id) { super(id); } @Override public double calculateSalary() { double totalSalary = 0; for (HumanResource humanResource : humanResources) { totalSalary += humanResource.calculateSalary(); } this.salary = totalSalary; return totalSalary; } public void addHumanResource(HumanResource humanResource) { humanResources.add(humanResource); } } /** * @description: 员工树叶构件 * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/3 */ public class Employee extends HumanResource{ public Employee(long id, double salary) { super(id); this.salary = salary; } @Override public double calculateSalary() { return salary; } }《设计模式之美》
http://c.biancheng.net/view/1373.html
《Java 设计模式》
《设计模式:可复用面向对象软件的基础》